Air filters for road tunnels
High filtering performance, easy maintenance, low operating costs and various installation options are the outstanding features of FILTRONtec air filters for road tunnels.
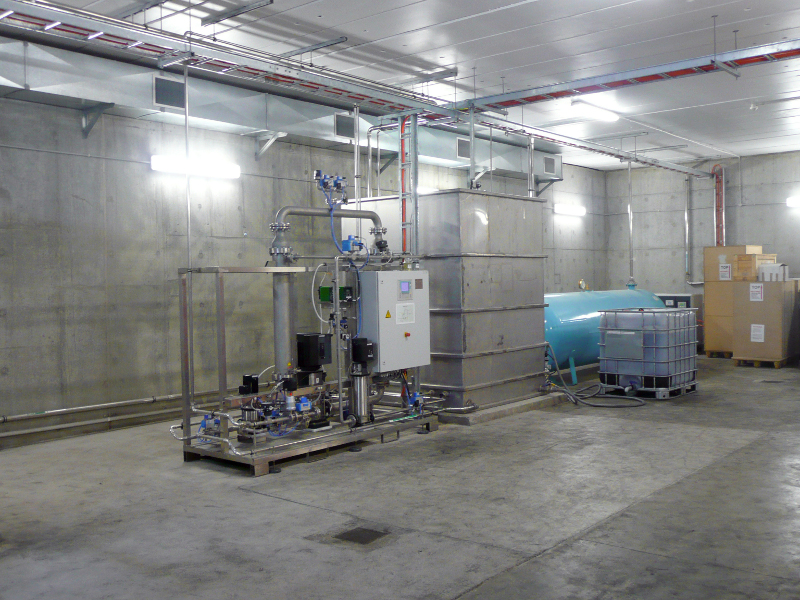
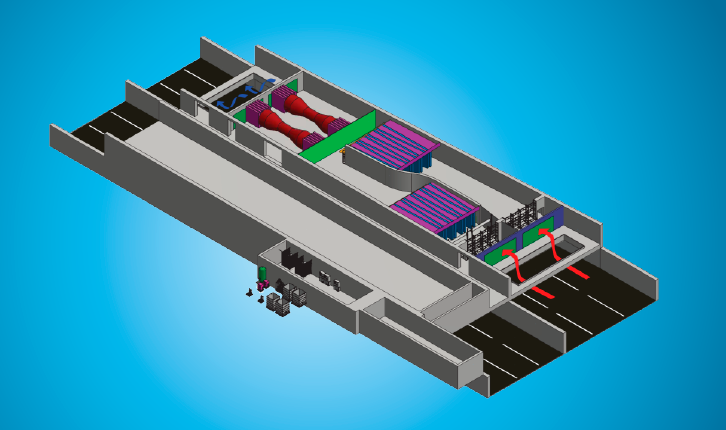
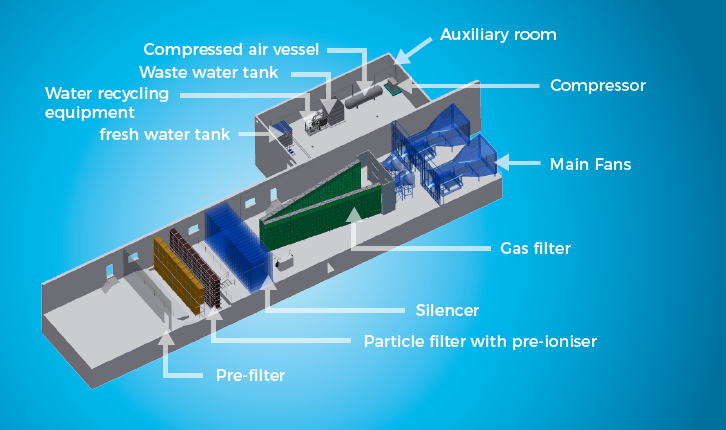
Function and construction of the filter system
The filter system consists of a particle filter and an activated carbon filter. While the particulate filter removes all impurities from the airflow, from large items of debris down to the smallest of particulate matter, the activated carbon filter reduces gaseous air pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide, ozone and benzenes.
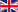
Deposition of fine dust in the particle filter
The air stream charged with fine dust passes through a multi-stage filter.
In a pre-filter, larger objects flying in the air, such as plastic bags and foliage, are first held back.
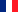
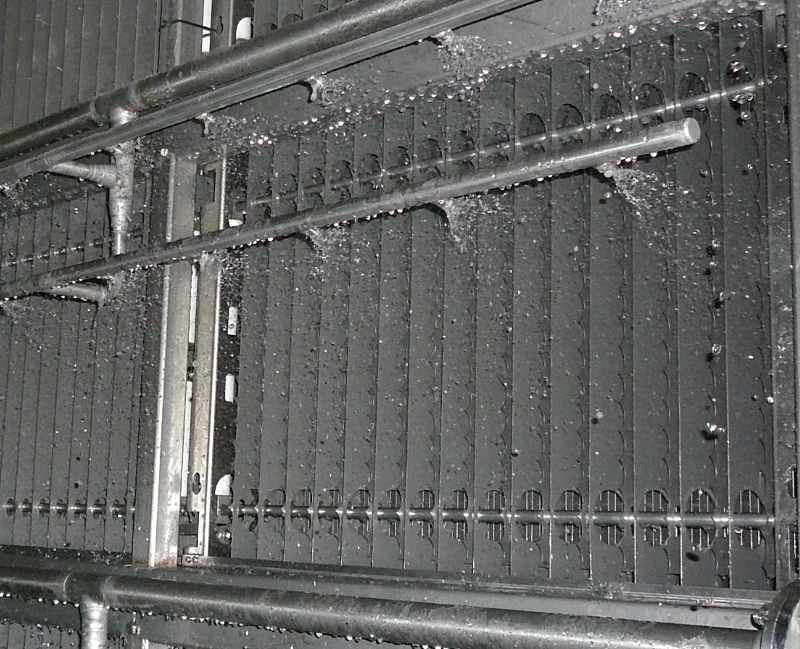
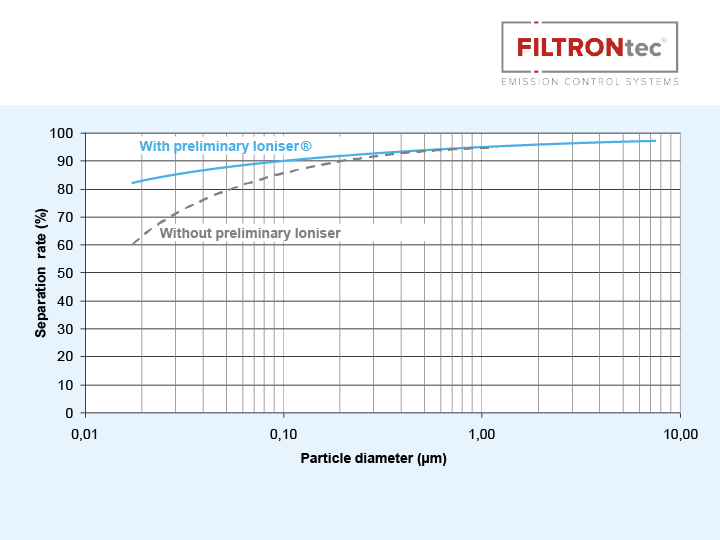
Subsequently, the air flows through a two-stage electrostatic precipitator (ESP). This consists of an ioniser and a collector (see figure on the right) and removes more than 85% of the soot and dust particles from the air stream. For this purpose, the particles are electrically charged in the ioniser before being deposited on the collector.
Once the collector plates of the ESP are loaded with dust, they are washed down with regular water using spray nozzles. During the cleaning process, the filter modules must be electrically disconnected and voltage-free. In order to keep the filter downtime as short as possible, it is pre-dried using compressed air via the existing spray nozzles. Alternatively, drying takes place during subsequent operation using the air flow. In this case our innovative soft start algorithm is used and investment and maintenance costs are reduced due to the elimination of the compressed air system. The control system of the filter system starts the cleaning process automatically. The cleaning sequence is fully automatic. It takes about 30 minutes and is usually scheduled during low traffic periods.
The dirty wash water with the filter deposits is cleaned in a water treatment plant and 90% of the employed water can be re-used for a new filter cleaning sequence.
The collected filter deposits can be evacuated to a landfill. Alternatively, due to the high carbon content, thermal use in a combustion plant can be considered. Depending on the sanitary water regulations, the collected wash water can often be disposed of directly with the other tunnel sewage waters.
The entire filtration process is environmentally friendly. No additives or other chemical auxiliaries, such as those that are frequently used for coagulation of filtrates in the wash water, are used for FILTRONtec filter systems.
Deposition of nitrogen dioxide
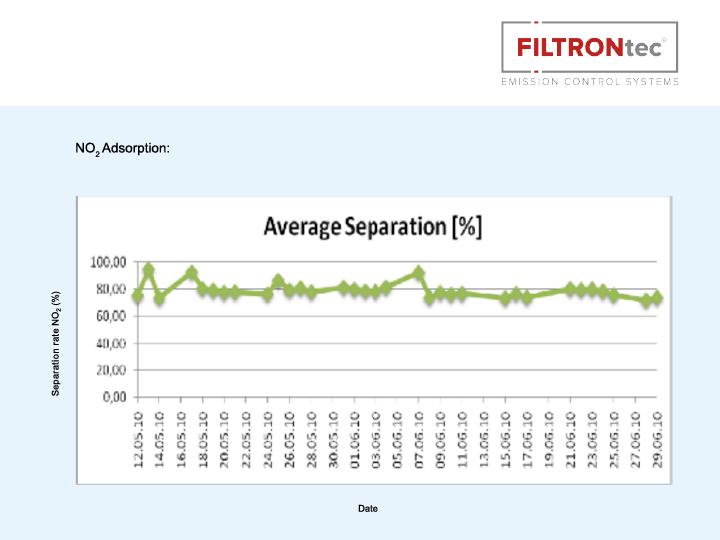
In order to remove harmful gases such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2), unburnt hydrocarbons (CmHn), ozone (O3) and benzenes from the exhaust air, an activated carbon filter can be arranged downstream of the particle filter. This retains up to 90% of the harmful gas components.
Activated carbon has a very high separation capacity for nitrogen dioxide and other gases.
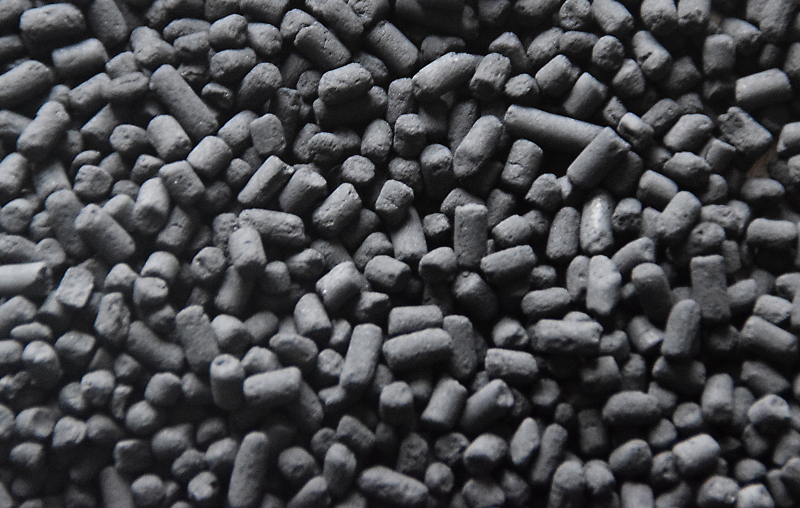
The specially treated activated carbon adsorbs nitrogen dioxide from the air stream. At the same time, part of the nitrogen dioxide is converted into harmless nitrogen and oxygen by catalytic dissociation in the filter. The filter carbon is formed into cylindrical rods, so-called pellets, with a diameter of 4 mm. Thanks to its porous structure, activated carbon has an enormous specific surface area, the active area of one gram of carbon being about 1,000 m².
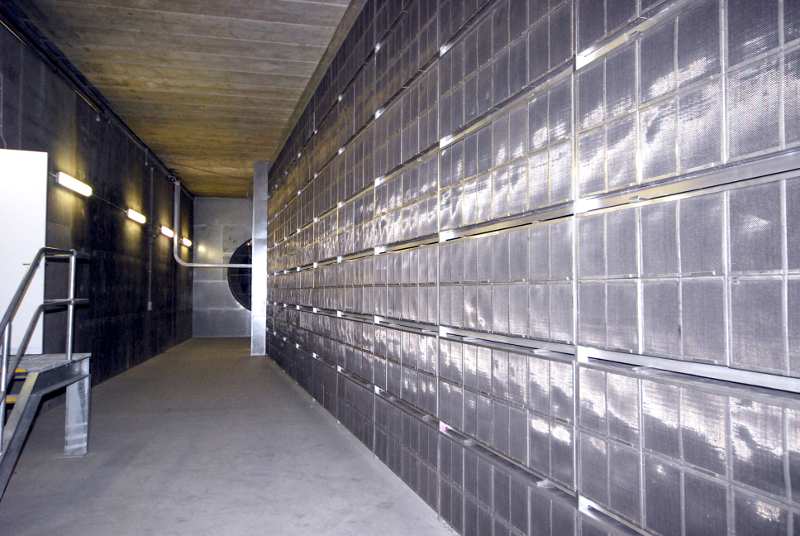
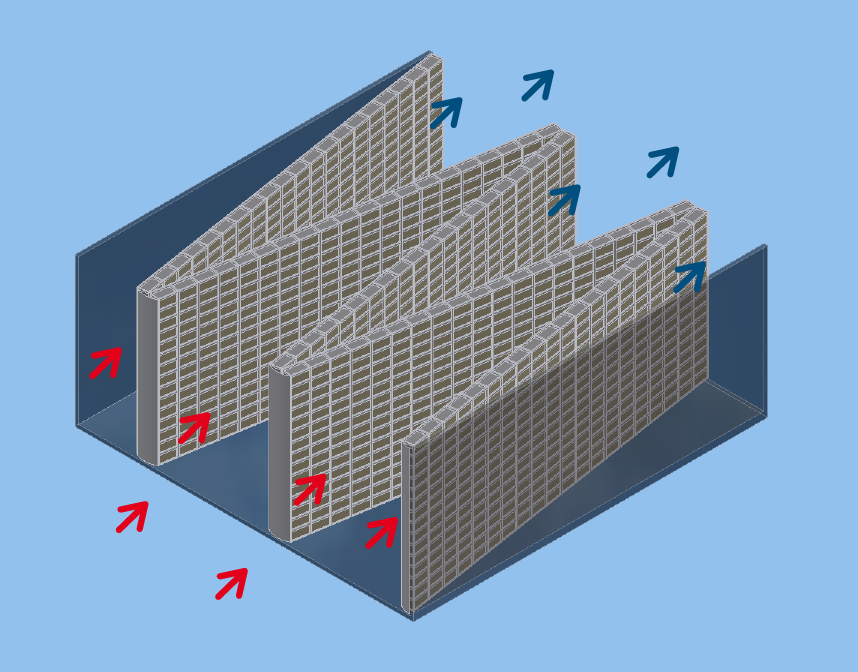
The gas filter is modular like the fine dust filter. The carbon pellets are filled in rectangular metal boxes with two opposite air-permeable perforated plates. The filled boxes are mounted next to each other on a vertical frame and thus form a closed filter wall. The exhaust air flows through the filter wall. In order to achieve optimum airflow, the filter walls in the air channel are arranged in a "W" shape.
If the separation capacity of activated carbon is exhausted after several years, the boxes are exchanged for newly filled boxes.
Alternatively, an installation with continuous filter walls is also possible.
Materials
All components and parts of the filter system that come into contact with the polluted exhaust air, such as the electrostatic precipitator, pre-ioniser, pipeline, nozzle and racks are made of high-quality stainless steel (V4A) with a long service life.
Behaviour of the air filter in case of fire
The most dangerous event that can happen in a tunnel is a fire. On the one hand, fire and smoke spread rapidly through the strong air currents in tunnel structures. On the other hand, the temperatures in the tunnel tube reach very high levels in a short time. In addition, smoke and toxic substances in the ever-longer tunnels make fire control and rescue work more difficult.
An optimal filter system can help to save lives. Therefore, the FILTRONtec particulate filters are designed to operate even at temperatures of 400°C. Smoke gases can be passed through the fine dust filter in the event of a fire. A fire test demonstrates in striking fashion that smoke particles with toxic substances are even retained in the filter for a limited time.

Operating costs
Fine dust filters and FILTRONtec gas filters consume very little electricity and water. This is because …
- the particulate matter particles are separated and deposited in an electrostatic field, with only a small current of a few milliampere (mA) flowing,
- the auxiliary units such as pumps, valves, air compressor are only operating for a short time every day during the cleaning sequence,
- the water is cleaned for the washing of the collector after the washing process and up to 90% of it is re-used, whereby only small losses due to evaporation or the residual moisture in the filtrate have to be replaced with fresh water,
- depending on the designed airflow velocity, the pressure loss of the FILTRONtec ESP filter can be of the order of about 100 Pascal and that of the activated carbon filter about 400 Pascal,
- the filtered exhaust air can escape to the outside at a low air velocity of only about 5 m/s, compared to as much as 20 m/s for a conventional ventilation system without filtering.
Operation, maintenance, conservation
FILTRONtec places strong emphasis on low downtimes, few and simple maintenance works and low conservation costs. That is why our air filter systems are designed for operation without constant supervision (MMO operation) – so they work on a fully automatic basis. All important functions can be monitored by the tunnel operations centre.
The filter system has only a few components with moving parts, such as standard pumps and valves as well as an air compressor, which have to be maintained according to the manufacturer's instructions.
A maintenance manual is provided, which describes in detail the intervals at which the safety devices have to be checked, cleaning carried out and other maintenance works conducted. No specialist personnel is required to operate the filter system.
The FILTRONtec gas filter consists only of static components and does not require any maintenance.
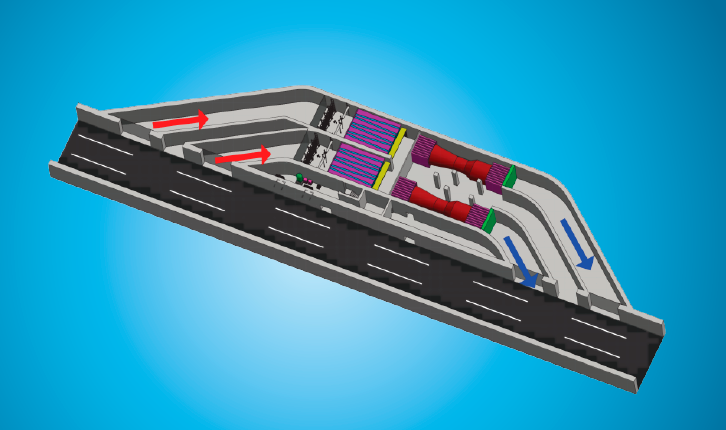
Installation examples of air filters in urban tunnels
Whether air filters for road tunnels are installed as a bypass in a tunnel interstitial space, in the tunnel ceiling or in a separate building depends on the local conditions. As a specialist in fine dust filters and gas filters, FILTRONtec is at your side when planning your air filter systems. Together we will find the technically and economically best solution for your application.
Installation as a bypass
When installed as a bypass, the filter system is installed in a gallery next to the roadway. The tunnel air is extracted from the tunnel by means of lateral openings in the tunnel wall. The openings are fitted with a grid.
After filtering, the cleaned air is returned to the area of the roadway or discharged into the environment.
Recessed ceiling
In the case of a ceiling installation, the filters are placed on an intermediate ceiling in the upper part of the tunnel tube. The contaminated air is sucked upwards from the tunnel and cleaned in the filter system.
The cleaned air is then fed back into the area of the roadway or discharged into the environment. This installation variant is particularly advantageous in road tunnels with a circular or oval cross-section of the tube.
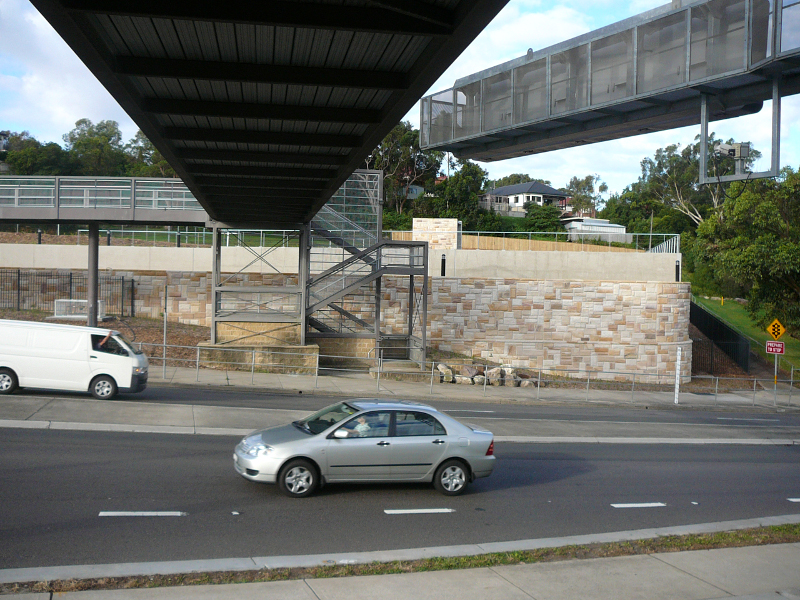
Installation in a separate filter building
If iIf it is not possible to install the air filter in the tunnel structure, the filter can be installed in a separate building nearby. The tunnel air is conveyed to the filter building via an air duct.
The purified air can either be re-circulated back to the tunnel via an air duct, or discharged from the filter building directly into the environment. An example of this type of installation is the FILTRONtec filter system in the M5-East tunnel in Sydney.
Air filter with switchable gas filter
The concentrations of fine dust and nitrogen dioxide in the ambient air can vary over the course of the day. While the measurements taken at a specific moment may show a high fine dust concentration and a low nitrogen dioxide value, later in the day a low fine dust content could be present at high nitrogen dioxide values. Furthermore, the NO2 concentration does not always have to be reduced in the total exhaust air quantity; it just has to meet the established NO2 limits.
FILTRONtec has therefore developed a system concept in which, depending on the concentration of nitrogen dioxide in the outside air, the gas filter can be switched on or off as required during the operation of the fine dust filter. This can further reduce the operating costs of the exhaust air filter.
This plant concept was implemented in 2010 in the M5-East tunnel in Sydney, Australia.
Retrofitting air filters
Given the right spatial conditions, which are very often present, our fine dust filters can be retrofitted into existing tunnels. The filter has a depth of only 1.60 m. Thanks to its modular design, the filter can be adapted to any room cross-section. The pressure loss of the filter is only 100 Pa. Changes to the exhaust fans are therefore not required.